|
“Stay hungry, Stay foolish” -- Steven Jobs Hi there! I am an senior undergraduate student from South China University of Technology. Now I am working closely with Prof.Ming-Hsuan Yang and
Dr. Yinxiao Li from Google DeepMind. I am working as a research intern in Bytedance, with Dr. Xuefeng Xiao and Dr. Yuxi Ren from Seed Team .
I was a visiting student in Stanford AI Lab.
I have also worked at Westlake University & OPPO Research Institude, focusing on Unified Multi-modal Understanding and Generation Model,
advised by Prof. Guo-Jun Qi (IEEE Fellow) .
Email: jinxiuliu0628@gmail.com / branodnjinxiuliu@cs.stanford.edu
Email / CV / Google Scholar |

Sidelights!!! Click the portrait 👆 and enjoy the animation magic from my project Prompt image to Life. |
|
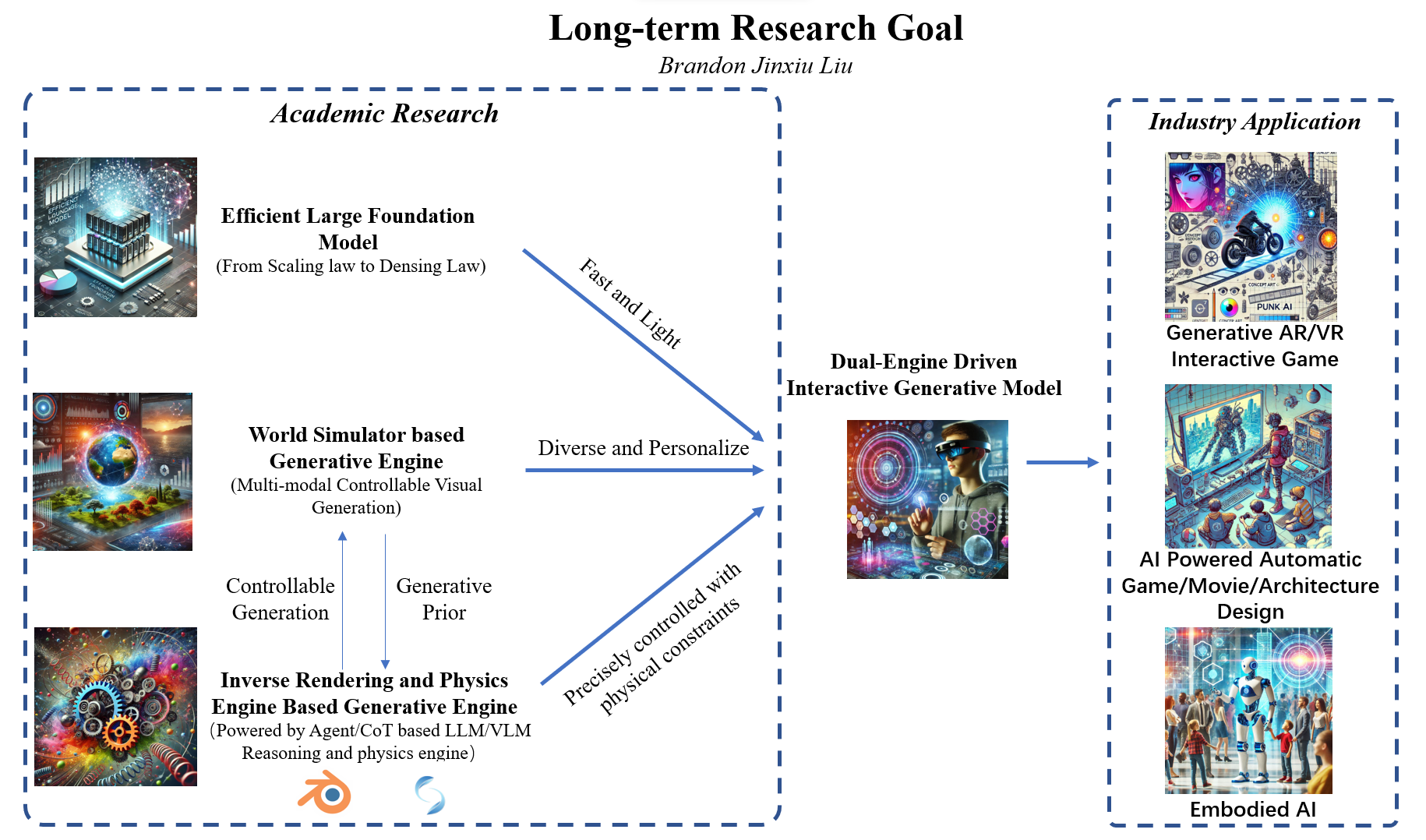
Recently I am considering how to develop an efficient and interactive world simulator with versatile applications in gaming, robotics, architecture, and physical simulations. This research is structured around three sub-goals, culminating in a dual-engine-driven simulator designed to optimize computational efficiency and interaction capabilities, even in resource-constrained and large-scale scenarios. Sub-Goal 1:Efficient Large Foundation Model A key challenge in generative models lies in their high computational demands. My research aims to address this by creating efficient foundation models that deliver fast inference, use fewer parameters, and maintain high-quality outputs. Techniques such as distillation, pruning, and quantization will be employed to optimize autoregressive video generation models. These advancements are particularly crucial for real-time applications in AR and XR, where low latency and scalability across resolutions are essential for delivering immersive experiences across diverse devices. Sub-Goal 2: World Simulator based Generative Engine This sub-goal focuses on building a world simulator capable of multi-modal, controllable visual generation while simulating complex world dynamics. The simulator will enable adaptive, interactive, and procedurally generated environments tailored to applications in gaming, robotics, and scientific research (AI4SCI). By integrating symbolic control and spatial reasoning, the system will dynamically adapt to user inputs and real-world constraints, enhancing interactivity, realism, and user engagement. Sub-Goal 3: Inverse Rendering and Physics Engine Based Generative Engine Bridging the gap between generative diversity and structural precision is critical for creating high-quality, editable 3D and 4D assets. My work will leverage inverse rendering and integrate physics engines, such as Blender, to produce assets with exceptional realism and precision. Furthermore, combining large language models (LLMs), vision-language models (VLMs), and agent-based symbolic frameworks will enable a flexible pipeline for asset generation, significantly reducing manual labor and enhancing creative workflows in industries like gaming and filmmaking. The Final Goal and Vision: Interactive Dual-Engine-Driven World Simulator and AIGC System By synthesizing these three sub-goals, my research aims to create a dual-engine-driven simulator that merges generative diversity with structural precision. This simulator will support dynamic, interactive, and highly realistic virtual environments, offering scalable solutions for applications in gaming, virtual testing, robotics, and AI-driven simulations. Ultimately, this work aspires to push the boundaries of interactive world simulation, driving both academic advancements and transformative real-world innovations. 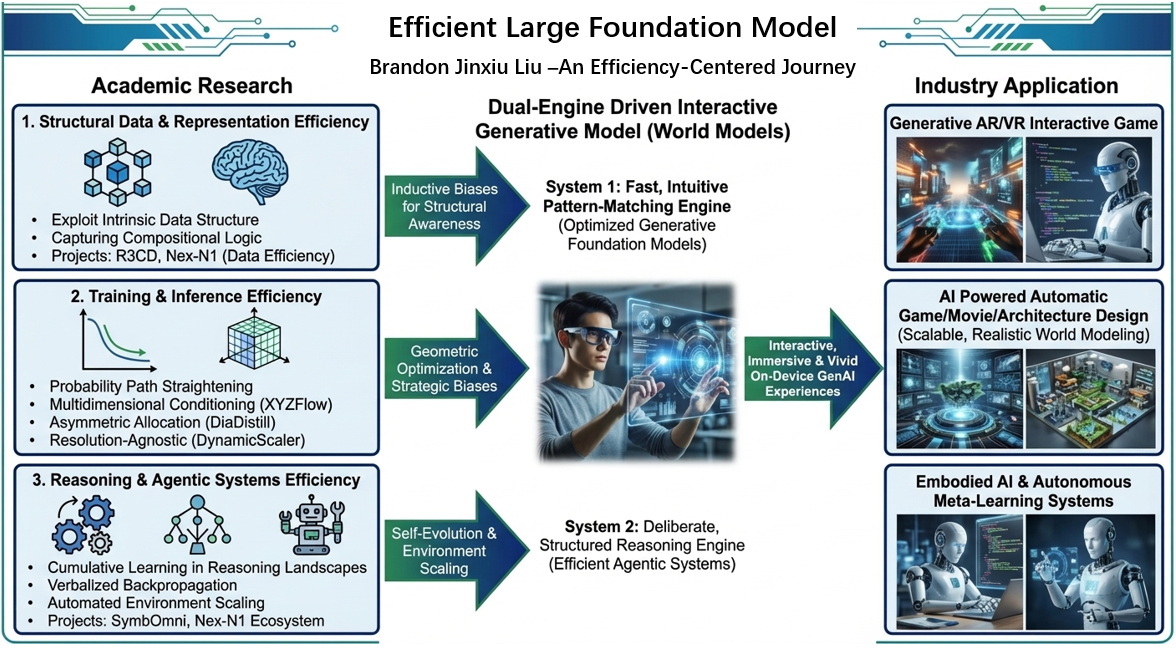
|
|
|

|
Nex-AGI TEAM , Research Scientist 2025/07 – Present
Focusing on Efficient Post-training Algorithm for LLM/MLLM and Efficient Agentic Systems. . | |
|
|
Bytedance (VideoGen Efficient Post-training Team) , Research Intern 2025/01 – 2025/07
Efficient Video generation . | |
|
|
Google DeepMind / UC Merced , Research Collaborator, supervised by Prof. Ming-Hsuan Yang and Dr. Yinxiao Li from Google DeepMind 2024/08 – 2024/11
High-quality Video generation . | |

|
Stanford AI Lab, Stanford University , Research Intern 06/24 – 08/24
Generative Spatial Intelligence. | |

|
Westlake University & OPPO Research Institude , Research Intern 2023/09 – 2024/6
Text driven Video Generation advised by Prof. Guo-Jun Qi (IEEE Fellow) . |
|
South China University of Technology (SCUT), Guangzhou, China 2021/09/21 – 2025/06/25
|
|
One paper is accepted by AAAI 2024 One paper is accepted by VDU@CVPR 2024 as Oral Presentation One paper is accepted by IJCAI 2024 One paper is featured as Hugging Face Daily Papers and reposted by AK . One paper is accepted by CVPR 2025, See you in Nashville! |
|
|
|
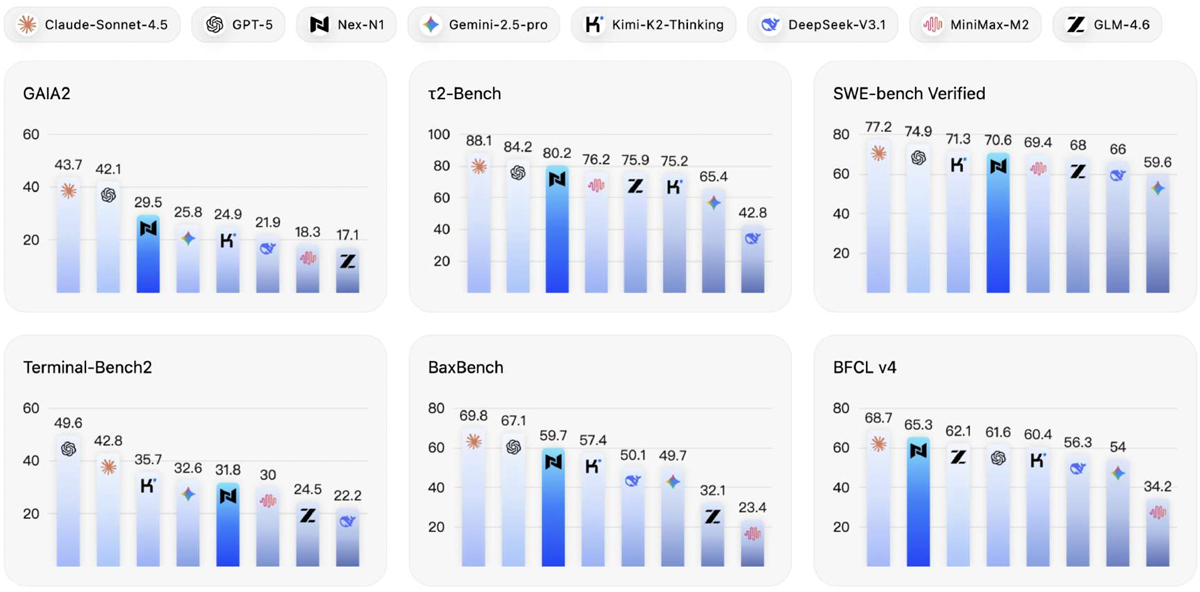
Nex-AGI TEAM (including Jinxiu Liu), The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) from passive responders to autonomous agents necessitates a fundamental shift in learning paradigms -- from static imitation to incentive-driven decision making. However, this transition is significantly impeded by the lack of scalable infrastructure capable of constructing high-quality interaction signals for effective policy learning. To address this, we introduce a comprehensive method designed to systematically scale the diversity and complexity of interactive environments. Our method realizes this scaling by addressing three orthogonal dimensions: (1) Complexity: NexAU, a flexible agent framework that supports building complex agent hierarchies via simple configurations; (2) Diversity: NexA4A automatically generates diverse agent hierarchies from natural language to cover infinite domains; and (3) Fidelity: NexGAP bridges the simulation-reality gap by integrating dynamic real-world environment for grounded trajectories synthesis. We train Nex-N1 upon the diverse and complex interactive environments established by our infrastructure. Empirical results on benchmarks such as SWE-bench and tau2 demonstrate that Nex-N1 consistently outperforms SOTA open-source models and achieves competitive performance against frontier proprietary models on complex agentic tasks. We open-source the Nex ecosystem and model weights to facilitate further research. Tech Report and Open Source Ecosystem Project Project page / / Paper |
|
|
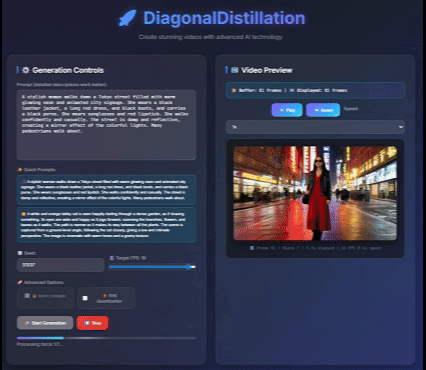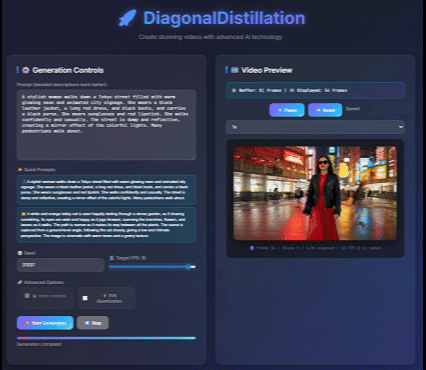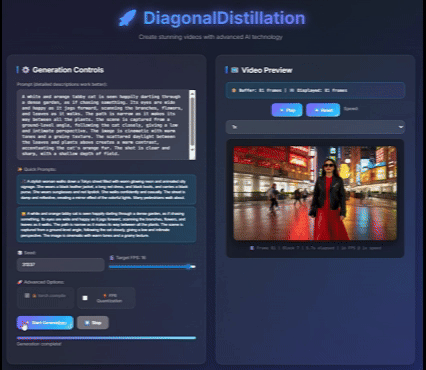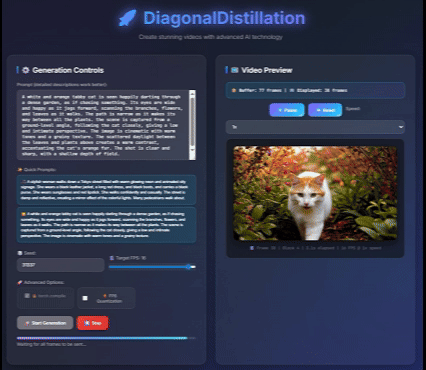
Jinxiu Liu*, Xuanming Liu*, Kangfu Mei, Yandong Wen, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Weiyang Liu, Large-scale pretrained diffusion models have significantly enhanced the quality of generated videos, and yet their use in real-time streaming remains limited. Autoregressive models offer a natural framework for sequential frame synthesis but require heavy computation to achieve high fidelity. Diffusion distillation can compress these models into efficient few-step variants, but existing video distillation approaches largely adapt image-specific methods that neglect temporal dependencies. These techniques often excel in image generation but underperform in video synthesis, exhibiting reduced motion coherence, error accumulation over long sequences, and a latency–quality trade-off. We identify two factors that result in these limitations: insufficient utilization of temporal context during step reduction and implicit prediction of subsequent noise levels in next-chunk prediction (exposure bias). To address these issues, we propose Diagonal Distillation, which operates orthogonally to existing approaches and better exploits temporal information across both video chunks and denoising steps. Central to our approach is an asymmetric generation strategy: more steps early, fewer steps later. This design allows later chunks to inherit rich appearance information from thoroughly processed early chunks, while using partially denoised chunks as conditional inputs for subsequent synthesis. By aligning the implicit prediction of subsequent noise levels during chunk generation with the actual inference conditions, our approach mitigates error propagation and reduces oversaturation in long-range sequences. We further incorporate implicit optical flow modeling to preserve motion quality under strict step constraints. Our method generates a 5-second video in just 2.61 seconds (up to 31 FPS), achieving a 277.3× speedup over the undistilled model and doubling the acceleration ratio of the state-of-the-art (140×) without sacrificing visual quality. ICLR 2026 under review Project page / |
|

|
Jinxiu Liu*, Shaoheng Lin*, Yinxiao Li, Ming-Hsuan Yang, The increasing demand for immersive AR/VR applications and spatial intelligence has heightened the need to generate high-quality scene-level and 360° panoramic video. However, most video diffusion models are constrained by limited resolution and aspect ratio, which restricts their applicability to scene-level dynamic content synthesis. In this work, we propose the DynamicScaler, addressing these challenges by enabling spatially scalable and panoramic dynamic scene synthesis that preserves coherence across panoramic scenes of arbitrary size. Specifically, we introduce a Offset Shifting Denoiser, facilitating efficient, synchronous, and coherent denoising panoramic dynamic scenes via a diffusion model with fixed resolution through a seamless rotating Window, which ensures seamless boundary transitions and consistency across the entire panoramic space, accommodating varying resolutions and aspect ratios. Additionally, we employ a Global Motion Guidance mechanism to ensure both local detail fidelity and global motion continuity. Extensive experiments demonstrate our method achieves superior content and motion quality in panoramic scene-level video generation, offering a training-free, efficient, and scalable solution for immersive dynamic scene creation with constant VRAM consumption regardless of the output video resolution. CVPR 2025 Paper / Code / project page / Huggingface Daily Papers |
|
|
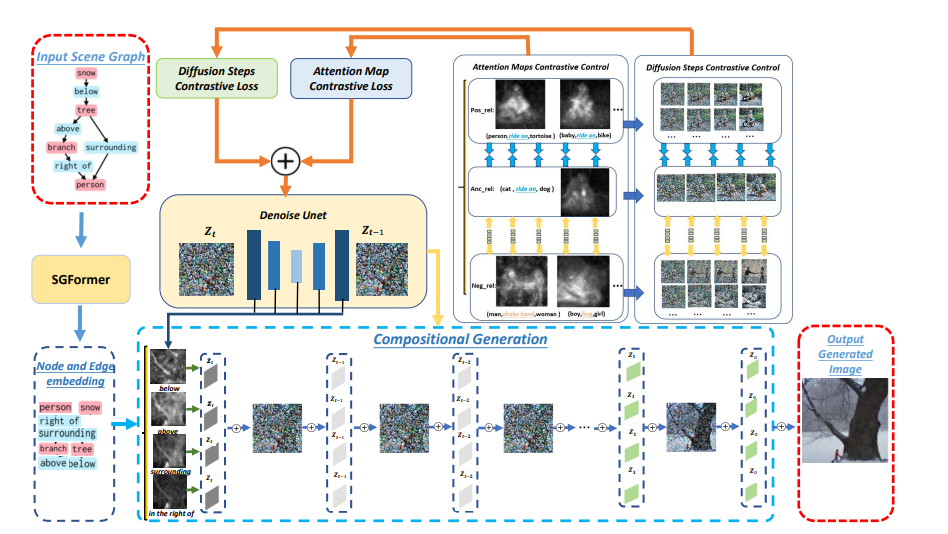
Jinxiu Liu, Qi Liu, In this paper, we introduce R3CD, a new image generation framework from scene graphs with large-scale diffusion models and contrastive control mechanisms. R3CD can handle complex or ambiguous relations in complex multi-object scene graphs and produce realistic and diverse images that match the scene graph specifications. R3CD consists of two main components: (1) SGFormer, a transformer-based encoder that captures both local and global information from scene graphs; (2) Relation-aware Diffusion contrastive control, a contrastive learning module that aligns the relation features and the image features across different levels of abstraction. AAAI 2024, 4 positive reviews Paper |
|
|
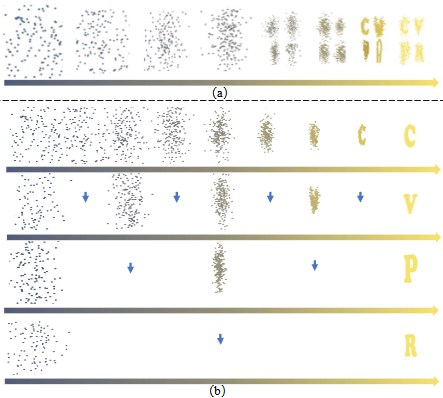
Jinxiu Liu*, Xuanming Liu*, Kangfu Mei, Yandong Wen, Weiyang Liu, The pursuit of high-fidelity image generation faces a fundamental trade-off between sampling speed and output quality. While diffusion models excel in quality, their iterative nature incurs high computational costs. Current efficient methods primarily focus on distilling pre-trained models into few-step samplers; however, this distillation process is challenging and heavily reliant on teacher model quality. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{\XYZFlow}, a novel framework that rethinks this paradigm through multidimensional scaling of flow matching. Unlike MeanFlow's single-step deterministic mapping, our approach intensively scales the expressive power of generative models by enhancing the uniqueness and learnability of probability paths through structured, multidimensional conditioning. Theoretically, we frame autoregressive modeling as an implicit flow straightening mechanism, where expanding contextual constraints reduce trajectory ambiguity. XYZFlow implements this via two orthogonal scaling dimensions: (1) \textit{Temporal scaling} through non-Markovian conditioning on the full denoising history, and (2) \textit{Spatial scaling} through next-shortcut prediction, where patches are generated sequentially using the complete denoising trajectories of preceding patches as priors. This multidimensional conditioning constructs a high-dimensional coordinate system for probability flows, enforcing mapping uniqueness. Extensive evaluations demonstrate XYZFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance, with 7.2--8.5 speedup over teachers while maintaining competitive FID. Notably, XYZFlow-B (172M) outperforms the one-step model MeanFlow-XL/2+ (676M), demonstrating that our structured shortcut design establishes a more parameter-efficient scaling dimension and achieves superior quality-latency trade-offs compared to simply enlarging models or compressing sampling steps. CVPR 2026 under review |
|
|
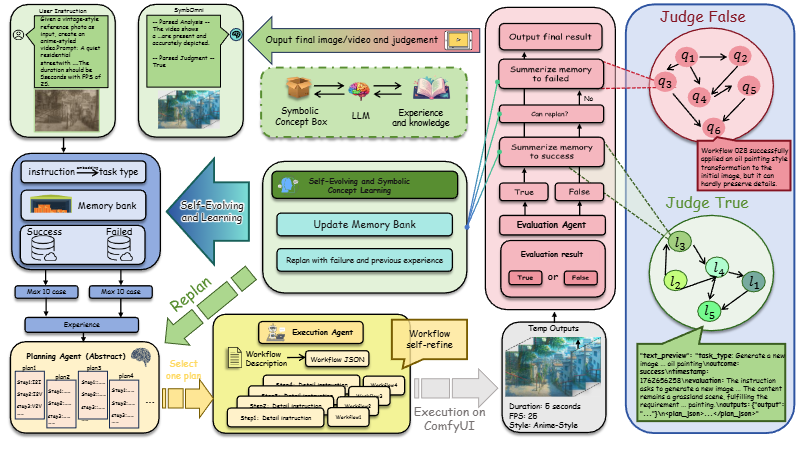
Jinxiu Liu*, Jianru Li*, Tanqing Kuang*, Xuanming Liu, Kangfu Mei, Yandong Wen, Weiyang Liu, Visual generation has witnessed rapidly expanding applications across diverse domains, ranging from text-to-image/video synthesis to interactive creation. However, prevailing monolithic models are fundamentally limited by an inability for cumulative learning and self-evolution (i.e., the "perpetual novice" problem), as they lack mechanisms to structure experiences into reusable knowledge and must instead rely on brittle, "from-scratch" reasoning, leading to poor compositional generalization and inefficient knowledge retention. To address these limitations, we introduce SymbOmni, an agentic omni model designed for cumulative evolution through Symbolic Concept Learning. Our architecture centers on the Symbolic Concept Box (CB)---an optimizable memory space that abstracts low-level operations into reusable Symbolic Workflow Instructions (SWIs). SymbOmni operates through an induction-transduction cycle: experiences are abstracted into symbolic concepts (induction), which are then strategically composed to solve novel tasks (transduction). This cycle is advanced by verbalized backpropagation, where a dual-verifier system generates language-based optimization signals to drive continuous self-improvement without gradient-based fine-tuning. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that SymbOmni achieves: (I) Superior Performance, significantly outperforming agent system for interative creation and leading closed-source models in both image quality and task success rates; (II) Enhanced Efficiency, reducing token consumption by over 30% while maintaining competitive generation quality; (III) Continuous Learning, demonstrating genuine cumulative improvement in online learning scenarios on ComfyBench, establishing a new state-of-the-art. CVPR 2026 under review |
|

|
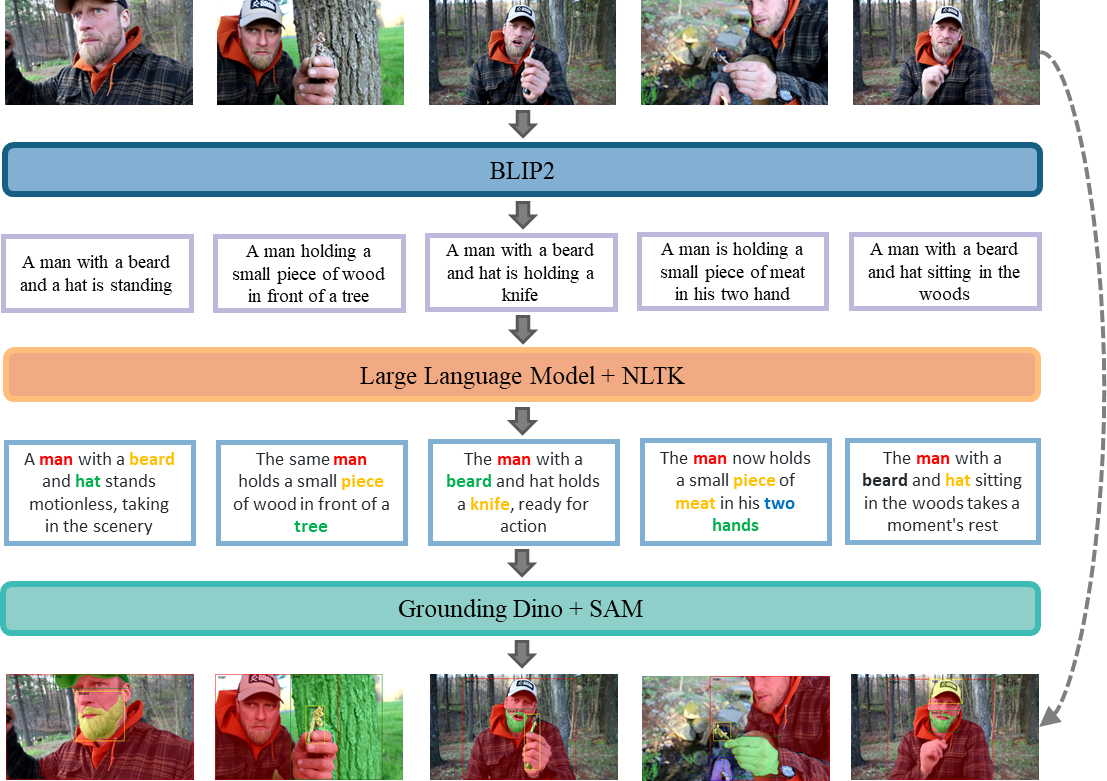
Zilyu Ye *, Jinxiu Liu * ‡ , Ruotian Peng * Jinjin Cao Zhiyang Chen Ziwei Xuan Mingyuan Zhou Xiaoqian Shen Mohamed Elhoseiny Qi Liu, Guo-Jun Qi (* contribute equally, ‡ Project Lead) Recent image generation models excel at creating high-quality images from brief captions. However, they fail to maintain consistency of multiple instances across images when encountering lengthy contexts. This inconsistency is largely due to in existing training datasets the absence of granular instance feature labeling in existing training datasets. To tackle these issues, we introduce Openstory++, a large-scale dataset combining additional instance-level annotations with both images and text. Furthermore, we develop a training methodology that emphasizes entity-centric image-text generation, ensuring that the models learn to effectively interweave visual and textual information. Specifically, Openstory++ streamlines the process of keyframe extraction from open-domain videos, employing vision-language models to generate captions that are then polished by a large language model for narrative continuity. It surpasses previous datasets by offering a more expansive open-domain resource, which incorporates automated captioning, high-resolution imagery tailored for instance count, and extensive frame sequences for temporal consistency. Additionally, we present Cohere-Bench, a pioneering benchmark framework for evaluating the image generation tasks when long multimodal context is provided, including the ability to keep the background, style, instances in the given context coherent. Compared to existing benchmarks, our work fills critical gaps in multi-modal generation, propelling the development of models that can adeptly generate and interpret complex narratives in open-domain environments. Experiments conducted within Cohere-Bench confirm the superiority of Openstory++ in nurturing high-quality visual storytelling models, enhancing their ability to address open-domain generation tasks. Tech Report, 🏆 Hugging Face Daily Papers Paper / Project Page (Code & Dataset) / |
|
|
Zilyu Ye *, Jinxiu Liu * ‡ , Jinjin Cao Zhiyang Chen Ziwei Xuan Mingyuan Zhou Qi Liu, Guo-Jun Qi (* contribute equally, ‡ Project Lead) In this paper, we present OpenStory, a large-scale dataset tailored for training subject-focused story visualization models to generate coherent and contextually relevant visual narratives. Addressing the challenges of maintaining subject continuityacross frames and capturing compelling narratives, We propose an innovative pipeline that automates the extraction ofkeyframes from open-domain videos. It ingeniously employsvision-language models to generate descriptive captions,which are then refined by a large language model to ensurenarrative flow and coherence. Furthermore, advanced sub-ject masking techniques are applied to isolate and segmentthe primary subjects. Derived from diverse video sources,including YouTube and existing datasets, OpenStory offersa comprehensive open-domain resource, surpassing priordatasets confined to specific scenarios. With automatedcaptioning instead of manual annotation, high-resolutionimagery optimized for subject count per frame, and exten-sive frame sequences ensuring consistent subjects for tem-poral modeling, OpenStory establishes itself as an invalu-able benchmark. It facilitates advancements in subject-focused story visualization, enabling the training of modelscapable of comprehending and generating intricate multi-modal narratives from extensive visual and textual inputs. CVPR 2024@VDU, Oral Presentation Paper / |
|

|
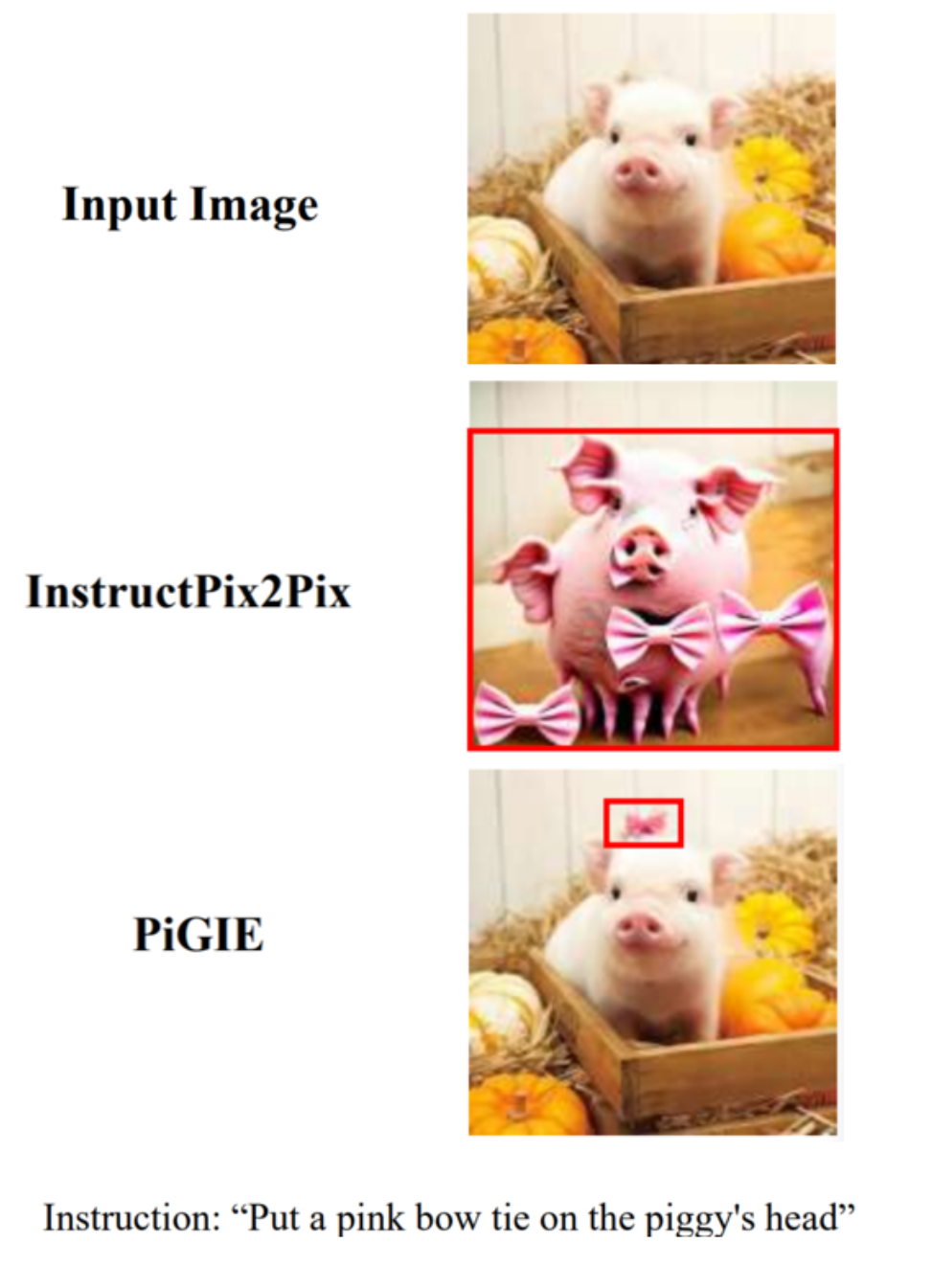
Tiancheng Li*, Jinxiu Liu* ‡, William Luo, Huajun Chen, Qi Liu, (* contribute equally, ‡ Project Lead) Instruction-based image editing is a challenging task since it requires to manipulation of the visual content of images according to complex human language instructions. When editing an image with tiny objects and complex positional relationships, existing image editing methods cannot locate the accurate region to execute the editing. To address this issue, we introduce Proximal Policy Optimization Guided Image Editing(PiGIE), a diffusion model that can accurately edit tiny objects in images with complex scenes. The PiGIE is able to incorporate proper noise masks to edit images based on the guidance of the target object’s attention maps. Different from the traditional image editing approaches based on supervised learning, PiGIE leverages the cosine similarity between UNet’s attention map and simulated human feedback as a reward function and employs Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) to fine-tune the diffusion model, such that PiGIE can locate the editing regions precisely based on human instructions. On multiple image editing benchmarks, PiGIE exhibits remarkable improvements in both mage quality and generalization capability. In particular, PiGIE sets a new baseline for editing fine-grained images with multiple tiny objects, shedding light on future studies on text-guided image editing for tiny objects. AI4CC@CVPR 2024 Extended Paper / Original Paper |
|
|
Bingwen Zhu, Fanyi Wang, Peng Liu, Jingwen Su, Jinxiu Liu, Yanhao Zhang, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang, Guo-Jun Qi, In this paper, we propose PoseAnimate, a novel zero-shot I2V framework for character animation.PoseAnimate contains three key components: 1) Pose-Aware Control Module (PACM) incorporates diverse pose signals into conditional embeddings, to preserve character-independent content and maintain precise alignment of actions.2) Dual Consistency Attention Module (DCAM) enhances temporal consistency, and retains character identity and intricate background details.3) Mask-Guided Decoupling Module (MGDM) refines distinct feature perception, improving animation fidelity by decoupling the character and background.We also propose a Pose Alignment Transition Algorithm (PATA) to ensure smooth action transition.Extensive experiment results demonstrate that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art training-based methods in terms of character consistency and detail fidelity. IJCAI 2024 Paper / project page |
|
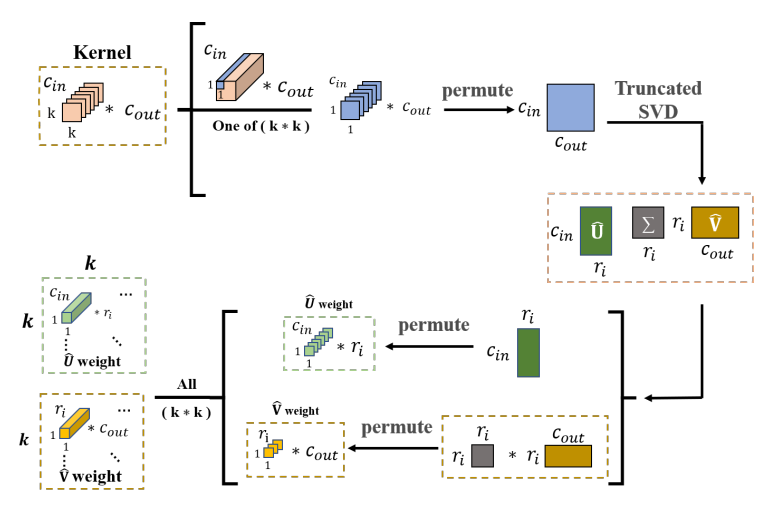
Xiaoye Zhu*, Jinxiu Liu*, Ye Liu, Michael NG, Zihan Ji, (* contribute equally) In this paper, we introduces a new method for compressing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) based on spatial-wise low-rank decomposition (SLR). The method preserves the higher-order structure of the filter weights and exploits their local low-rankness in different spatial resolutions, which can be implemented as a 1x1 convolution layer and achieves significant reductions in model size and computation cost with minimal accuracy loss. The paper shows the superior performance of the method over state-of-the-art low-rank compression methods and network pruning methods on several popular CNNs and datasets. Best Project (1/96) in "Optimization Method Course Project" |
|
|

|
Course Design of Deep Learning and Computer Vision mentored by Prof. Mingkui Tan and Prof. Huiping Zhuang, - Took LLM as an API that calls other large-scale models based on natural language instructions. - Developed a text-based dialogue system based on ChatGLM that can call for three large-scale models for image captioning, image generation, and text conversation using natural language commands by instruction finetuning. - Provided a webui interface based on gradio for easy interaction with the system and showcased various examples of its capabilities. Awarded as the Best Course Design, 1/39 project report |
|
|
|
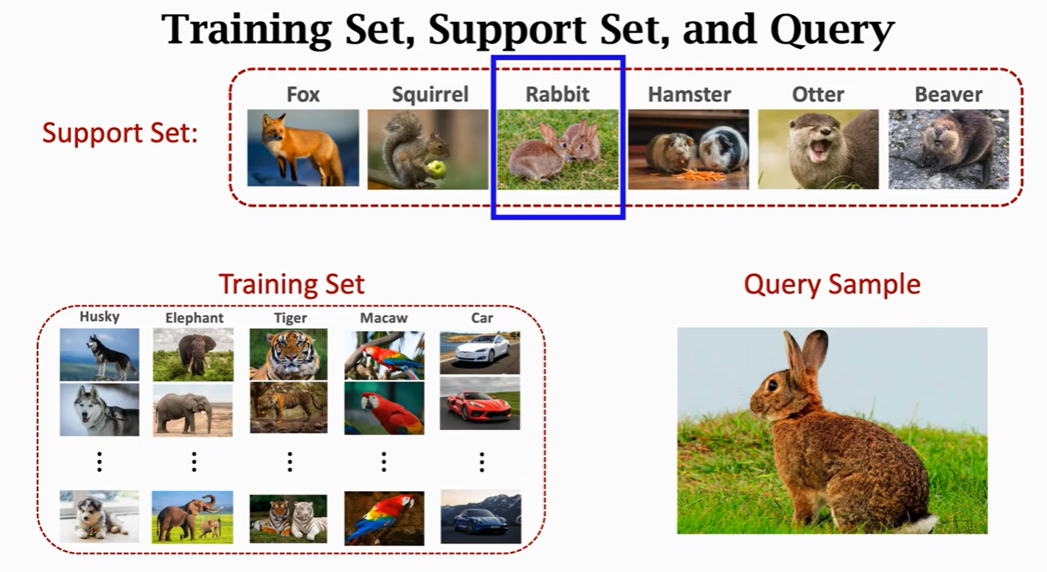
Honored to be invited by Xinjie Shen, Chairman of AIA(Artificial Intelligence Association) in SCUT. In this talk, I explore the use of few-shot learning techniques for RE based on my research experience. I introduce the basic concepts and principles of few-shot learning, such as the meta-learning framework, the episodic training strategy, and the evaluation metrics. I also discuss some recent advances and applications of few-shot learning for RE, such as the use of pre-trained language models, graph neural networks, contrastive learning, and data augmentation. I demonstrate how few-shot learning can improve the performance and robustness of RE models on different datasets and scenarios. I also share some of the challenges and future directions of few-shot learning for RE. Slides |
|
|
|
Template from Jon Barron. |